728x90
반응형
레이스 컨디션 (Race Condition)
레이스 컨디션은 두 개 이상의 스레드가 동시에 공유자원에 접근하여 실행 순서에 따라 예상치 않은 결과를 발생함을 의미한다.
class Callme {
void call(String msg) {
System.out.print("[" + msg);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Interrupted");
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}
class Caller implements Runnable {
String msg;
Callme target;
Thread t;
public Caller(Callme targ, String s) {
target = targ;
msg = s;
t = new Thread(this);
}
public void run() {
target.call(msg);
}
}
class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Callme target = new Callme();
Caller ob1 = new Caller(target, "Hello");
Caller ob2 = new Caller(target, "World");
ob1.t.start();
ob2.t.start();
try {
ob1.t.join();
ob2.t.join();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Interrupted");
}
}
}
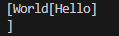
위 코드처럼 작성한다면 ob2의 t가 실행되는 와중에 ob1의 t가 실행되어 다음과 같은 결과가 발생할 수 있다.
스레드 동기화 (synchronized)
따라서 두 개 이상의 스레드가 공유 자원을 접근 시 하나의 스레드만 자원을 사용하도록 보장할 필요가 있다.
이때 스레드 동기화를 통해 monitor를 자동으로 관리하여 스레드 간 상호 배제를 구현할 수 있게 된다.
Java는 언어 레벨에서 synchronized 키워드를 사용하여 동기화를 지원한다.
synchronized 키워드를 사용하면 코드에 임계영역(Critical Section)을 설정하여 스레드가 임계영역에 진입하면 락을 설정한다. 다른 스레드는 락이 풀릴 때까지 해당 영역에 접근할 수 없고 대기해야 한다.
class Callme {
synchronized void call(String msg) {
System.out.print("[" + msg);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Interrupted");
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}
class Caller implements Runnable {
String msg;
Callme target;
Thread t;
public Caller(Callme targ, String s) {
target = targ;
msg = s;
t = new Thread(this);
}
public void run() {
target.call(msg);
}
}
class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Callme target = new Callme();
Caller ob1 = new Caller(target, "Hello");
Caller ob2 = new Caller(target, "World");
ob1.t.start();
ob2.t.start();
try {
ob1.t.join();
ob2.t.join();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Interrupted");
}
}
}
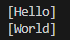
위 코드를 통해 두 스레드가 자원을 동시에 사용하지 않고 의도한 대로 실행되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
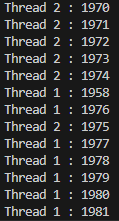
class Counter {
private int count = 0;
public synchronized void increment() {
count++;
}
public int GetCount() {
return count;
}
}
class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Counter cnt = new Counter();
Runnable myrun1 = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
cnt.increment();
System.out.println("Thread 1 : " + cnt.GetCount());
}
}
};
Runnable myrun2 = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
cnt.increment();
System.out.println("Thread 2 : " + cnt.GetCount());
}
}
};
Thread t1 = new Thread(myrun1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(myrun2);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println("Final count : " + cnt.GetCount());
}
}
728x90
반응형
'Java > Java 문법' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 박싱, 언박싱, 래퍼클래스(Wrapper Class), Integer, Character (0) | 2024.12.01 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 열거형 (enum) (0) | 2024.12.01 |
| [Java] 스레드(Thread), 모니터(Monitor), Runnable 인터페이스 (0) | 2024.10.27 |
| [Java] 예외 처리 (검사형 예외, 비검사형 예외) (0) | 2024.10.27 |
| [Java] Iterator 인터페이스 (0) | 2024.10.14 |

